RybackQualification N0Qualification N0 obtenue dans le cursus tronc commun (T-45C) de l'ESCAQualification N1 - UH-1HQualification N1 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N2 - UH-1HQualification N2 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N3 - UH-1HQualification N3 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCA100 Heures de VolSeuil de 100 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCA500 Heures de VolSeuil de 500 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCA1000 Heures de VolSeuil de 1000 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCAPilote de la 8e Escadre de Chasse VirtuelleA publié suffisament de messages sur le forum pour accéder au contenu réservé aux membres de l'école et de la 8e EscadreQualification N1 - A-10C IIQualification N1 obtenue dans le cursus A-10C II de l'ESCA300 SujetsMembre ayant publié un message dans plus de 300 sujets différents2500 Heures de VolSeuil de 2500 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCAVoltigeur aérienMembre ayant fait partie de l'une des patrouilles acrobatiques de l'ESCA
RybackQualification N0Qualification N0 obtenue dans le cursus tronc commun (T-45C) de l'ESCAQualification N1 - UH-1HQualification N1 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N2 - UH-1HQualification N2 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N3 - UH-1HQualification N3 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCA100 Heures de VolSeuil de 100 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCA500 Heures de VolSeuil de 500 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCA1000 Heures de VolSeuil de 1000 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCAPilote de la 8e Escadre de Chasse VirtuelleA publié suffisament de messages sur le forum pour accéder au contenu réservé aux membres de l'école et de la 8e EscadreQualification N1 - A-10C IIQualification N1 obtenue dans le cursus A-10C II de l'ESCA300 SujetsMembre ayant publié un message dans plus de 300 sujets différents2500 Heures de VolSeuil de 2500 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCAVoltigeur aérienMembre ayant fait partie de l'une des patrouilles acrobatiques de l'ESCA



Localisation : Argenteuil/Castelginest
Messages : 678
Date d'inscription : 11/09/2020
 Symbologie IHADSS
Symbologie IHADSS
Mar 14 Nov 2023 - 8:57
Killight et Rushman aiment ce message
 RybackQualification N0Qualification N0 obtenue dans le cursus tronc commun (T-45C) de l'ESCAQualification N1 - UH-1HQualification N1 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N2 - UH-1HQualification N2 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N3 - UH-1HQualification N3 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCA100 Heures de VolSeuil de 100 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCA500 Heures de VolSeuil de 500 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCA1000 Heures de VolSeuil de 1000 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCAPilote de la 8e Escadre de Chasse VirtuelleA publié suffisament de messages sur le forum pour accéder au contenu réservé aux membres de l'école et de la 8e EscadreQualification N1 - A-10C IIQualification N1 obtenue dans le cursus A-10C II de l'ESCA300 SujetsMembre ayant publié un message dans plus de 300 sujets différents2500 Heures de VolSeuil de 2500 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCAVoltigeur aérienMembre ayant fait partie de l'une des patrouilles acrobatiques de l'ESCA
RybackQualification N0Qualification N0 obtenue dans le cursus tronc commun (T-45C) de l'ESCAQualification N1 - UH-1HQualification N1 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N2 - UH-1HQualification N2 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N3 - UH-1HQualification N3 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCA100 Heures de VolSeuil de 100 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCA500 Heures de VolSeuil de 500 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCA1000 Heures de VolSeuil de 1000 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCAPilote de la 8e Escadre de Chasse VirtuelleA publié suffisament de messages sur le forum pour accéder au contenu réservé aux membres de l'école et de la 8e EscadreQualification N1 - A-10C IIQualification N1 obtenue dans le cursus A-10C II de l'ESCA300 SujetsMembre ayant publié un message dans plus de 300 sujets différents2500 Heures de VolSeuil de 2500 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCAVoltigeur aérienMembre ayant fait partie de l'une des patrouilles acrobatiques de l'ESCA



Localisation : Argenteuil/Castelginest
Messages : 678
Date d'inscription : 11/09/2020
 Re: Symbologie IHADSS
Re: Symbologie IHADSS
Mar 14 Nov 2023 - 9:07
Killight, Matoche et Rushman aiment ce message
 RybackQualification N0Qualification N0 obtenue dans le cursus tronc commun (T-45C) de l'ESCAQualification N1 - UH-1HQualification N1 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N2 - UH-1HQualification N2 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N3 - UH-1HQualification N3 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCA100 Heures de VolSeuil de 100 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCA500 Heures de VolSeuil de 500 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCA1000 Heures de VolSeuil de 1000 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCAPilote de la 8e Escadre de Chasse VirtuelleA publié suffisament de messages sur le forum pour accéder au contenu réservé aux membres de l'école et de la 8e EscadreQualification N1 - A-10C IIQualification N1 obtenue dans le cursus A-10C II de l'ESCA300 SujetsMembre ayant publié un message dans plus de 300 sujets différents2500 Heures de VolSeuil de 2500 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCAVoltigeur aérienMembre ayant fait partie de l'une des patrouilles acrobatiques de l'ESCA
RybackQualification N0Qualification N0 obtenue dans le cursus tronc commun (T-45C) de l'ESCAQualification N1 - UH-1HQualification N1 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N2 - UH-1HQualification N2 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N3 - UH-1HQualification N3 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCA100 Heures de VolSeuil de 100 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCA500 Heures de VolSeuil de 500 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCA1000 Heures de VolSeuil de 1000 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCAPilote de la 8e Escadre de Chasse VirtuelleA publié suffisament de messages sur le forum pour accéder au contenu réservé aux membres de l'école et de la 8e EscadreQualification N1 - A-10C IIQualification N1 obtenue dans le cursus A-10C II de l'ESCA300 SujetsMembre ayant publié un message dans plus de 300 sujets différents2500 Heures de VolSeuil de 2500 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCAVoltigeur aérienMembre ayant fait partie de l'une des patrouilles acrobatiques de l'ESCA



Localisation : Argenteuil/Castelginest
Messages : 678
Date d'inscription : 11/09/2020
 Re: Symbologie IHADSS
Re: Symbologie IHADSS
Mar 14 Nov 2023 - 9:14
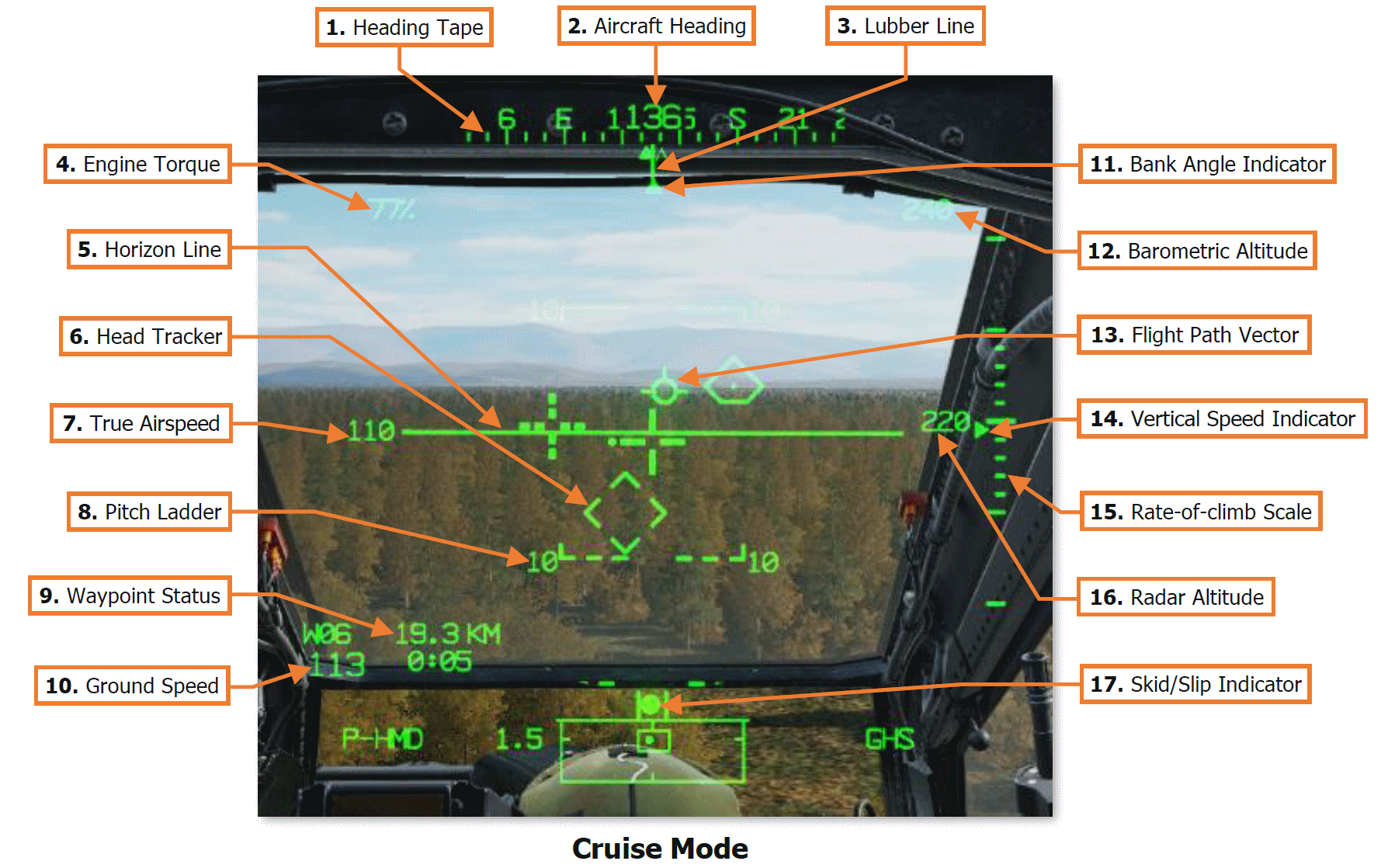
1. Heading Tape. Displays a 180° hemisphere of magnetic headings. Major tick marks are displayed in 30° increments and marked by a cardinal direction or heading in the tens value. Minor tick marks are displayed in 10° increments.
2. Aircraft Heading. Displays a digital readout of the aircraft’s current magnetic heading in 1° increments, superimposed over the Heading Tape.
3. Lubber Line. The Lubber Line is aligned to the centerline of the aircraft and serves as a reference for both the aircraft heading and for the Bank Angle Indicator when in Cruise symbology mode.
4. Engine Torque. Displays the highest torque value of the two engines, in 1% increments. A box will be displayed around the torque at 98% or greater. If the difference in engine torque values exceeds 12%, the torque digital readout will flash.
5. Horizon Line. Indicates the horizon position and orientation relative to the aircraft nose, which is referenced to the LOS Reticle.
When in Cruise symbology mode, the the Horizon Line is displaced in pitch in a 2:1 movement ratio.
When in Transition symbology mode, the Horizon Line is displaced in pitch in a 4:1 movement ratio, up to a maximum of ±30°. When aircraft pitch attitude exceeds ±30° in pitch, the Transition mode Horizon Line will remain saturated at maximum deflection until the pitch attitude is less than ±30°.
6. Head Tracker. Represents the armament datum line (ADL, or centerline) of the aircraft; 0° in azimuth and -4.9° in elevation. The Head Tracker assists the crewmembers in maintaining awareness of their head position relative to the nose of the aircraft, especially under low-light conditions while using the PNVS or TADS sensors for flight and navigation.
7. True Airspeed. Indicates the true airspeed (TAS) of the aircraft in 1 knot increments, from 0 to 210 knots. The airspeed indication is boxed if the airspeed exceeds VNE.
When Attitude Hold is engaged, a rounded “status window” box is displayed around the TAS digital readout.
8. Pitch Ladder. Indicates aircraft pitch attitude when in Cruise symbology mode. Pitch ladder increments are displayed at ±10°, ±20°, ±30°, ±45° and ±60° pitch.
9. Waypoint Status. Displays the point selected for navigation, its distance in kilometers or nautical miles, and estimated time enroute (ETE). The ETE is based on the current ground speed and distance remaining, and is presented in HH:MM format when the ETE is ≥5 minutes, or M:SS format when ETE is <5 minutes.
The ETE is not displayed when ground speed is <15 knots or ETE is >10 hours. Waypoint Status information is not displayed if there is no active destination point.
10. Ground Speed. Indicates the speed across the surface in 1 knot increments. Ground Speed is only displayed in Cruise and Transition symbology modes, and only when the primary INU is aligned.
11. Bank Angle Indicator. Indicates bank angle relative to the horizon when in Cruise symbology mode. When the Bank Angle Indicator is aligned with the lubber line below the heading tape, the aircraft is in a level attitude.
12. Barometric Altitude. Indicates the barometric altitude when Cruise mode symbology is displayed. Barometric Altitude is displayed in 10-foot increments from -2,300 feet to 20,000 feet.
13. Flight Path Vector. The Flight Path Vector (FPV) represents the point towards which the helicopter is flying. It is a 3-dimensional representation of the aircraft’s velocity vector. The FPV is not displayed in Hover or Bob-Up symbology modes, if the 3-dimensional velocity is <5 knots ground speed, or if the aircraft is weight-on-wheels.
14. Vertical Speed Indicator (VSI). The Vertical Speed Indicator moves up and down the rate-of-climb scale to indicate vertical speed. The VSI becomes saturated at the ±1,000 fpm tick marks at the top or bottom of the Rate-of-climb Scale, augmented by digital readouts of rate-of-climb in 100 fpm increments.
15. Rate-of-climb Scale. Major tick marks are placed at 0, ±500 and ±1,000 feet per minute (fpm) rates of climb/descent. Minor tick marks are placed in 100 fpm increments between 0 and ±500 fpm. When the rate-of-climb/descent exceeds ±1,000 fpm, a digital readout to the nearest 100 fpm value is displayed adjacent to the 1,000 fpm major tick marks.
When Altitude Hold is engaged, a rounded “homeplate” box is displayed next to the Rate-of-climb Scale at 0 fpm.
16. Radar Altitude. Indicates the radar-detected altitude above ground level from 0 to 1,428 feet. The Radar Altitude is displayed in increments of 1 foot from 0 to 50 feet in altitude, and increments of 10 feet between 50 feet and 1,428 feet in altitude.
The Radar Altitude is not displayed when the altitude exceeds 1,428 feet above ground level.
17. Skid/Slip Indicator. Also called the “trim ball”; indicates whether the aircraft is in coordinated flight (also known as “in aerodynamic trim”, or simply “in trim”). With the ball is centered between the tick marks, the aircraft is in coordinated flight, which minimizes drag. If the ball is left of center, applying left pedal will adjust tail rotor thrust to bring the aircraft back into coordinated flight. Likewise, if the ball is right of center, applying right pedal will adjust tail rotor thrust to bring the aircraft back into coordinated flight.
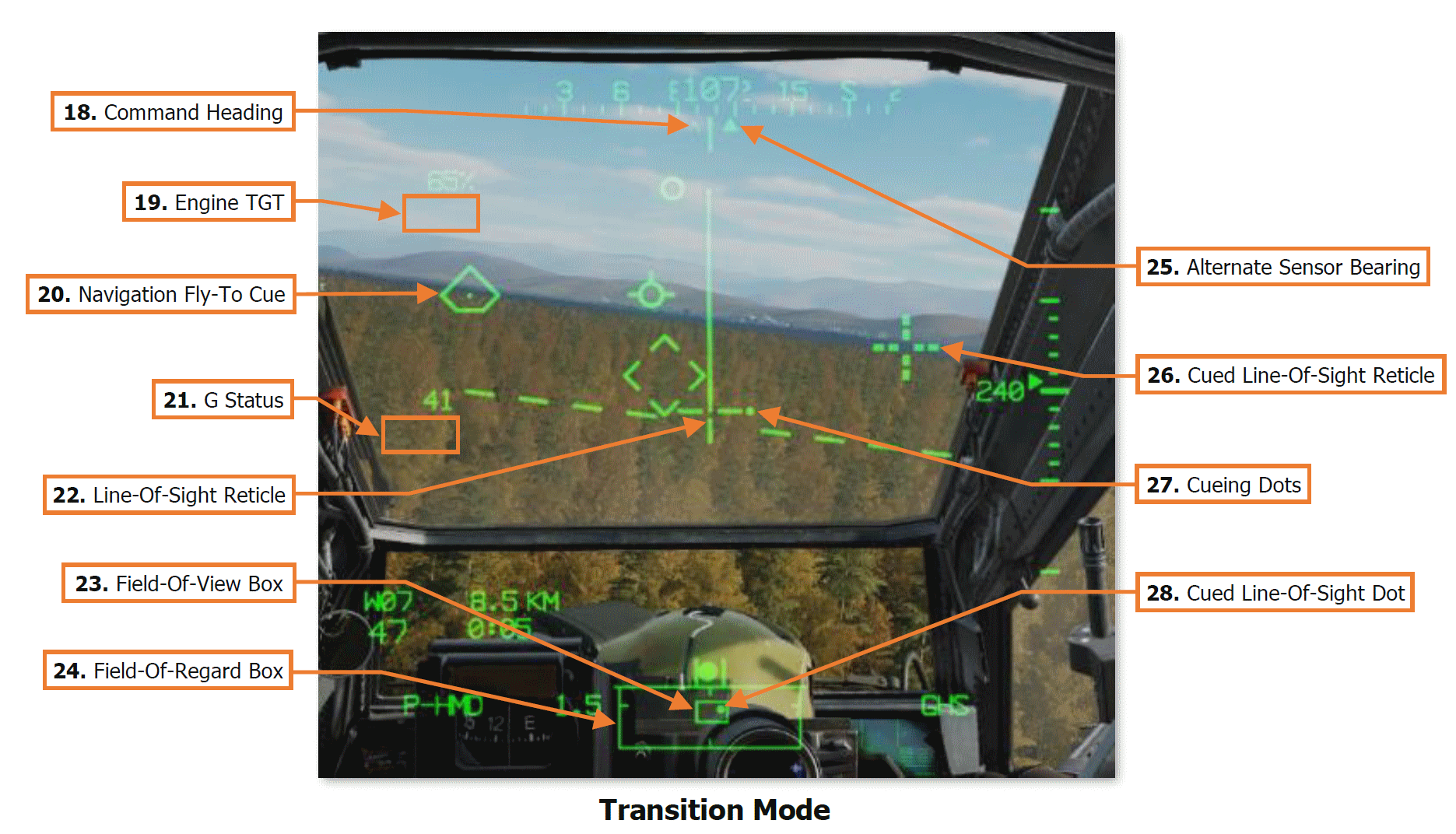
18. Command Heading. Indicates the magnetic heading to the Navigation Fly-To Cue when in Cruise, Transition, or Hover symbology modes. When Bob-up symbology mode is entered, the Command Heading chrevron is set to the heading of the aircraft, and maintained at that value until Bob-Up mode is exited.
19. Engine TGT. Displays the highest of the two engines’ Turbine Gas Temperature (TGT) indications if operating in an intermediate or contingency TGT limit.
When operating under dual engine intermediate power, the TGT (in °C) will be displayed during the final two minutes of either the 30-minute or 10-minute allowable timers.
When operating under single engine contingency power, the TGT (in °C) will be displayed during the entire 2.5 minutes allowable for operating in the contingency power temperature range.
20. Line-Of-Sight (LOS) Reticle. Indicates the crewmember’s helmet line-of-sight (LOS). The LOS Reticle is used as a positional reference for the Head Tracker, Horizon Line, Velocity Vector, Acceleration Cue, and Bob-Up Box. It is also used as an aiming crosshair for weapons employment, and is bolded when in Cruise symbology mode.
The LOS Reticle flashes when the crewmember’s LOS is invalid, the selected NVS sensor is at its slew limit, or if the gun is actioned and the gun system has failed and is no longer following the crewmember’s helmet.
21. Navigation Fly-To Cue. Indicates the location of the current point selected for navigation. Also called the “homeplate” symbol, the Navigation Fly-To Cue is sized so the Flight Path Vector fits within it for precise 3-dimensional navigation.
The Navigation Fly-To Cue is not displayed when the aircraft is weight-on-wheels.
22. G Status. Displays the accelerometer measured G-force on the aircraft when the load factor exceeds 2G’s, or if within ¼G of the G load factor limit under the current conditions of velocity, density altitude, and gross weight.
23. Field-Of-View (FOV) Box. The FOV box indicates the relative position of the crewmember’s helmet line-of-sight within the larger Field-of-Regard box. The FOV box represents a 30° x 40° field of view and is driven by the crewmember’s helmet orientiation as detected by helmet sensors within each resepective cockpit.
24. Field-Of-Regard (FOR) Box. The FOR box indicates azimuth limits for the crewmember’s Night Vision System (NVS) sensor turret. The format of the FOR box is determined by the NVS sensor (PNVS or TADS) assigned to that crewstation. Tick marks around the edges of the PNVS FOR box mark 0° in azimuth and elevation. Tick marks around the edges of the TADS FOR box mark 0° and ±90° in azimuth, and 0° elevation.
25. Alternate Sensor Bearing. Indicates the magnetic heading of the opposite crewmember’s selected sight when the opposite crewmember’s sight is HMD or TADS.
The Alternate Sensor Bearing symbol is not displayed when the other crewmember’s selected sight is FCR.
26. Cued Line-Of-Sight Reticle. Indicates the virtual location of the crewmember’s selected acquisition source.
If CUEING is deselected on the Pilot’s WPN Utility (UTIL) sub-page, this symbol is not displayed.
27. Cueing Dots. Indicates the quadrant direction of the selected acquisition source to “cue” the crewmember’s helmet position to the location of the Cued LOS Reticle. The dots are removed when the Cued LOS Reticle is with 4° of that quadrant relative to the LOS Reticle.
All four dots flash when the “IHADSS B/S REQUIRED” message is present within the Sight Status field of the High Action Display, indicating the crewmember needs to boresight their IHADSS.
If CUEING is deselected on the Pilot’s WPN Utility (UTIL) sub-page, these dots are not displayed.
28. Cued Line-Of-Sight Dot. Indicates the relative location of the selected acquisition source within the Field-of-Regard box.
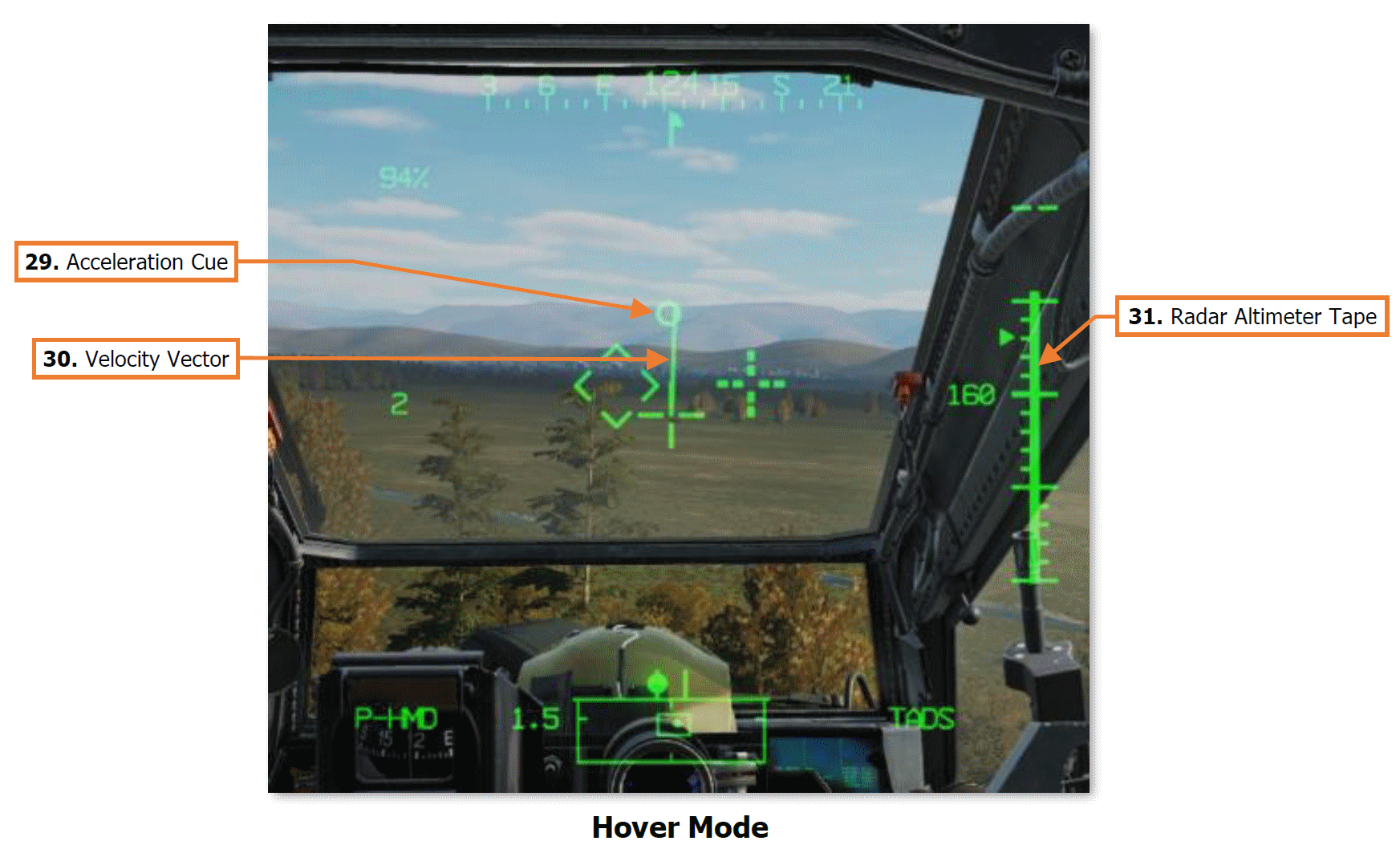
29. Acceleration Cue. The Acceleration Cue indicates magnitude and direction of the aircraft’s rate of acceleration. The Acceleration Cue is displayed in Transition, Hover, and Bob-Up symbology modes.
When in Transition mode, or in Hover or Bob-Up modes when the ground speed is <6 knots, the Acceleration Cue is displaced from the outer point of the Velocity Vector. When in Hover or Bob-Up modes and the Velocity Vector becomes “saturated” at 6 knots ground speed, the Acceleration Cue displacement originates from the center of the LOS reticle.
30. Velocity Vector. The Velocity Vector indicates the aircraft’s 2-dimensional direction and magnitude of velocity across the surface.
In Hover and Bob-Up symbology modes, the Velocity Vector will become “saturated” (reaching it’s maximum displacement) at 6 knots ground speed. In Transition symbology mode, the Velocity Vector will become saturated at 60 knots ground speed.
31. Radar Altimeter Tape. The Radar Altimeter Tape displays altitude above ground level in an “analog” format. Major tick marks are displayed in 50-foot increments between 0 and 200 feet. Minor tick marks are displayed in 10-foot increments between 0 and 50 feet.
96
When the aircraft has exceeded 200 feet AGL, the Radar Altimeter Tape will be removed from the symbology. The Radar Altimeter Tape will not be subsequently displayed until the aircraft descends below 180 feet AGL.
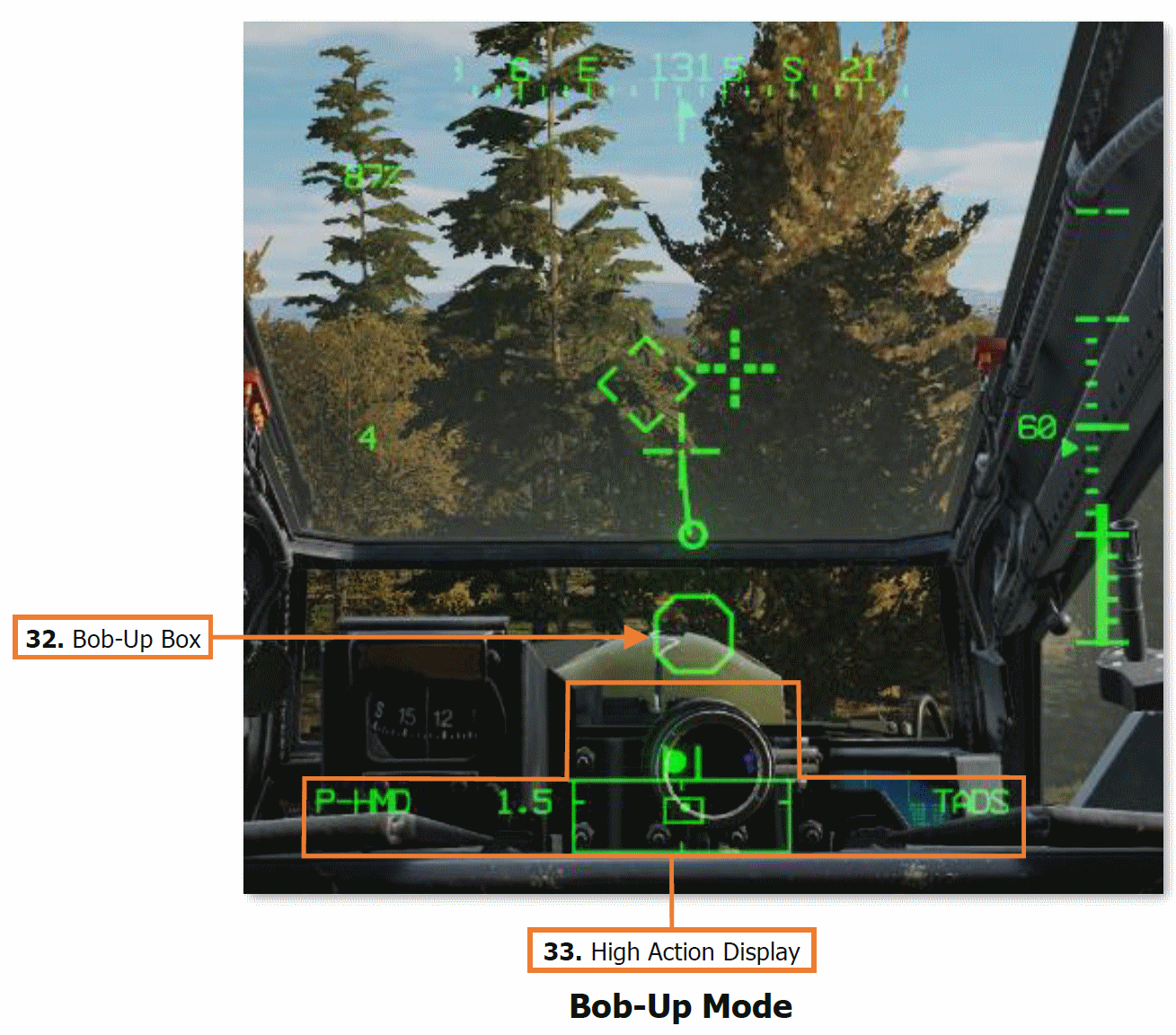
32. Bob-Up Box. The Bob-Up Box represents a 12-foot wide octogonal box anchored to a position on the surface below the helicopter.
When Bob-Up symbology mode is entered, the Bob-Up Box is displayed and referenced to the 2-dimensional position on the surface the helicopter was located over when Bob-Up mode was entered. This is termed “dropping a Bob-Up box”. The box will remain in this position until the crew changes symbology modes.
As the aircraft moves laterally across the surface, the Bob-Up Box moves within the symbology to indicate the relative position of the reference location. When the Bob-Up box has become “saturated” (reaching it’s maximum displacement), the aircraft has displaced 40 feet from the reference position on the surface. Once the aircraft returns to within 40 feet of the reference position, the Bob-Up Box will become de-saturated.
33. High Action Display. The High Action Display is displayed in both Flight and Weapons symbology. The HAD provides prioritized sight and weapon status messages to the crew for targeting and weapons employment. (See High Action Display in the Helmet-Mounted Display chapter for more information.)
2. Aircraft Heading. Displays a digital readout of the aircraft’s current magnetic heading in 1° increments, superimposed over the Heading Tape.
3. Lubber Line. The Lubber Line is aligned to the centerline of the aircraft and serves as a reference for both the aircraft heading and for the Bank Angle Indicator when in Cruise symbology mode.
4. Engine Torque. Displays the highest torque value of the two engines, in 1% increments. A box will be displayed around the torque at 98% or greater. If the difference in engine torque values exceeds 12%, the torque digital readout will flash.
5. Horizon Line. Indicates the horizon position and orientation relative to the aircraft nose, which is referenced to the LOS Reticle.
When in Cruise symbology mode, the the Horizon Line is displaced in pitch in a 2:1 movement ratio.
When in Transition symbology mode, the Horizon Line is displaced in pitch in a 4:1 movement ratio, up to a maximum of ±30°. When aircraft pitch attitude exceeds ±30° in pitch, the Transition mode Horizon Line will remain saturated at maximum deflection until the pitch attitude is less than ±30°.
6. Head Tracker. Represents the armament datum line (ADL, or centerline) of the aircraft; 0° in azimuth and -4.9° in elevation. The Head Tracker assists the crewmembers in maintaining awareness of their head position relative to the nose of the aircraft, especially under low-light conditions while using the PNVS or TADS sensors for flight and navigation.
7. True Airspeed. Indicates the true airspeed (TAS) of the aircraft in 1 knot increments, from 0 to 210 knots. The airspeed indication is boxed if the airspeed exceeds VNE.
When Attitude Hold is engaged, a rounded “status window” box is displayed around the TAS digital readout.
8. Pitch Ladder. Indicates aircraft pitch attitude when in Cruise symbology mode. Pitch ladder increments are displayed at ±10°, ±20°, ±30°, ±45° and ±60° pitch.
9. Waypoint Status. Displays the point selected for navigation, its distance in kilometers or nautical miles, and estimated time enroute (ETE). The ETE is based on the current ground speed and distance remaining, and is presented in HH:MM format when the ETE is ≥5 minutes, or M:SS format when ETE is <5 minutes.
The ETE is not displayed when ground speed is <15 knots or ETE is >10 hours. Waypoint Status information is not displayed if there is no active destination point.
10. Ground Speed. Indicates the speed across the surface in 1 knot increments. Ground Speed is only displayed in Cruise and Transition symbology modes, and only when the primary INU is aligned.
11. Bank Angle Indicator. Indicates bank angle relative to the horizon when in Cruise symbology mode. When the Bank Angle Indicator is aligned with the lubber line below the heading tape, the aircraft is in a level attitude.
12. Barometric Altitude. Indicates the barometric altitude when Cruise mode symbology is displayed. Barometric Altitude is displayed in 10-foot increments from -2,300 feet to 20,000 feet.
13. Flight Path Vector. The Flight Path Vector (FPV) represents the point towards which the helicopter is flying. It is a 3-dimensional representation of the aircraft’s velocity vector. The FPV is not displayed in Hover or Bob-Up symbology modes, if the 3-dimensional velocity is <5 knots ground speed, or if the aircraft is weight-on-wheels.
14. Vertical Speed Indicator (VSI). The Vertical Speed Indicator moves up and down the rate-of-climb scale to indicate vertical speed. The VSI becomes saturated at the ±1,000 fpm tick marks at the top or bottom of the Rate-of-climb Scale, augmented by digital readouts of rate-of-climb in 100 fpm increments.
15. Rate-of-climb Scale. Major tick marks are placed at 0, ±500 and ±1,000 feet per minute (fpm) rates of climb/descent. Minor tick marks are placed in 100 fpm increments between 0 and ±500 fpm. When the rate-of-climb/descent exceeds ±1,000 fpm, a digital readout to the nearest 100 fpm value is displayed adjacent to the 1,000 fpm major tick marks.
When Altitude Hold is engaged, a rounded “homeplate” box is displayed next to the Rate-of-climb Scale at 0 fpm.
16. Radar Altitude. Indicates the radar-detected altitude above ground level from 0 to 1,428 feet. The Radar Altitude is displayed in increments of 1 foot from 0 to 50 feet in altitude, and increments of 10 feet between 50 feet and 1,428 feet in altitude.
The Radar Altitude is not displayed when the altitude exceeds 1,428 feet above ground level.
17. Skid/Slip Indicator. Also called the “trim ball”; indicates whether the aircraft is in coordinated flight (also known as “in aerodynamic trim”, or simply “in trim”). With the ball is centered between the tick marks, the aircraft is in coordinated flight, which minimizes drag. If the ball is left of center, applying left pedal will adjust tail rotor thrust to bring the aircraft back into coordinated flight. Likewise, if the ball is right of center, applying right pedal will adjust tail rotor thrust to bring the aircraft back into coordinated flight.
18. Command Heading. Indicates the magnetic heading to the Navigation Fly-To Cue when in Cruise, Transition, or Hover symbology modes. When Bob-up symbology mode is entered, the Command Heading chrevron is set to the heading of the aircraft, and maintained at that value until Bob-Up mode is exited.
19. Engine TGT. Displays the highest of the two engines’ Turbine Gas Temperature (TGT) indications if operating in an intermediate or contingency TGT limit.
When operating under dual engine intermediate power, the TGT (in °C) will be displayed during the final two minutes of either the 30-minute or 10-minute allowable timers.
When operating under single engine contingency power, the TGT (in °C) will be displayed during the entire 2.5 minutes allowable for operating in the contingency power temperature range.
20. Line-Of-Sight (LOS) Reticle. Indicates the crewmember’s helmet line-of-sight (LOS). The LOS Reticle is used as a positional reference for the Head Tracker, Horizon Line, Velocity Vector, Acceleration Cue, and Bob-Up Box. It is also used as an aiming crosshair for weapons employment, and is bolded when in Cruise symbology mode.
The LOS Reticle flashes when the crewmember’s LOS is invalid, the selected NVS sensor is at its slew limit, or if the gun is actioned and the gun system has failed and is no longer following the crewmember’s helmet.
21. Navigation Fly-To Cue. Indicates the location of the current point selected for navigation. Also called the “homeplate” symbol, the Navigation Fly-To Cue is sized so the Flight Path Vector fits within it for precise 3-dimensional navigation.
The Navigation Fly-To Cue is not displayed when the aircraft is weight-on-wheels.
22. G Status. Displays the accelerometer measured G-force on the aircraft when the load factor exceeds 2G’s, or if within ¼G of the G load factor limit under the current conditions of velocity, density altitude, and gross weight.
23. Field-Of-View (FOV) Box. The FOV box indicates the relative position of the crewmember’s helmet line-of-sight within the larger Field-of-Regard box. The FOV box represents a 30° x 40° field of view and is driven by the crewmember’s helmet orientiation as detected by helmet sensors within each resepective cockpit.
24. Field-Of-Regard (FOR) Box. The FOR box indicates azimuth limits for the crewmember’s Night Vision System (NVS) sensor turret. The format of the FOR box is determined by the NVS sensor (PNVS or TADS) assigned to that crewstation. Tick marks around the edges of the PNVS FOR box mark 0° in azimuth and elevation. Tick marks around the edges of the TADS FOR box mark 0° and ±90° in azimuth, and 0° elevation.
25. Alternate Sensor Bearing. Indicates the magnetic heading of the opposite crewmember’s selected sight when the opposite crewmember’s sight is HMD or TADS.
The Alternate Sensor Bearing symbol is not displayed when the other crewmember’s selected sight is FCR.
26. Cued Line-Of-Sight Reticle. Indicates the virtual location of the crewmember’s selected acquisition source.
If CUEING is deselected on the Pilot’s WPN Utility (UTIL) sub-page, this symbol is not displayed.
27. Cueing Dots. Indicates the quadrant direction of the selected acquisition source to “cue” the crewmember’s helmet position to the location of the Cued LOS Reticle. The dots are removed when the Cued LOS Reticle is with 4° of that quadrant relative to the LOS Reticle.
All four dots flash when the “IHADSS B/S REQUIRED” message is present within the Sight Status field of the High Action Display, indicating the crewmember needs to boresight their IHADSS.
If CUEING is deselected on the Pilot’s WPN Utility (UTIL) sub-page, these dots are not displayed.
28. Cued Line-Of-Sight Dot. Indicates the relative location of the selected acquisition source within the Field-of-Regard box.
29. Acceleration Cue. The Acceleration Cue indicates magnitude and direction of the aircraft’s rate of acceleration. The Acceleration Cue is displayed in Transition, Hover, and Bob-Up symbology modes.
When in Transition mode, or in Hover or Bob-Up modes when the ground speed is <6 knots, the Acceleration Cue is displaced from the outer point of the Velocity Vector. When in Hover or Bob-Up modes and the Velocity Vector becomes “saturated” at 6 knots ground speed, the Acceleration Cue displacement originates from the center of the LOS reticle.
30. Velocity Vector. The Velocity Vector indicates the aircraft’s 2-dimensional direction and magnitude of velocity across the surface.
In Hover and Bob-Up symbology modes, the Velocity Vector will become “saturated” (reaching it’s maximum displacement) at 6 knots ground speed. In Transition symbology mode, the Velocity Vector will become saturated at 60 knots ground speed.
31. Radar Altimeter Tape. The Radar Altimeter Tape displays altitude above ground level in an “analog” format. Major tick marks are displayed in 50-foot increments between 0 and 200 feet. Minor tick marks are displayed in 10-foot increments between 0 and 50 feet.
96
When the aircraft has exceeded 200 feet AGL, the Radar Altimeter Tape will be removed from the symbology. The Radar Altimeter Tape will not be subsequently displayed until the aircraft descends below 180 feet AGL.
32. Bob-Up Box. The Bob-Up Box represents a 12-foot wide octogonal box anchored to a position on the surface below the helicopter.
When Bob-Up symbology mode is entered, the Bob-Up Box is displayed and referenced to the 2-dimensional position on the surface the helicopter was located over when Bob-Up mode was entered. This is termed “dropping a Bob-Up box”. The box will remain in this position until the crew changes symbology modes.
As the aircraft moves laterally across the surface, the Bob-Up Box moves within the symbology to indicate the relative position of the reference location. When the Bob-Up box has become “saturated” (reaching it’s maximum displacement), the aircraft has displaced 40 feet from the reference position on the surface. Once the aircraft returns to within 40 feet of the reference position, the Bob-Up Box will become de-saturated.
33. High Action Display. The High Action Display is displayed in both Flight and Weapons symbology. The HAD provides prioritized sight and weapon status messages to the crew for targeting and weapons employment. (See High Action Display in the Helmet-Mounted Display chapter for more information.)
Killight et Matoche aiment ce message
 RybackQualification N0Qualification N0 obtenue dans le cursus tronc commun (T-45C) de l'ESCAQualification N1 - UH-1HQualification N1 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N2 - UH-1HQualification N2 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N3 - UH-1HQualification N3 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCA100 Heures de VolSeuil de 100 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCA500 Heures de VolSeuil de 500 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCA1000 Heures de VolSeuil de 1000 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCAPilote de la 8e Escadre de Chasse VirtuelleA publié suffisament de messages sur le forum pour accéder au contenu réservé aux membres de l'école et de la 8e EscadreQualification N1 - A-10C IIQualification N1 obtenue dans le cursus A-10C II de l'ESCA300 SujetsMembre ayant publié un message dans plus de 300 sujets différents2500 Heures de VolSeuil de 2500 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCAVoltigeur aérienMembre ayant fait partie de l'une des patrouilles acrobatiques de l'ESCA
RybackQualification N0Qualification N0 obtenue dans le cursus tronc commun (T-45C) de l'ESCAQualification N1 - UH-1HQualification N1 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N2 - UH-1HQualification N2 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N3 - UH-1HQualification N3 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCA100 Heures de VolSeuil de 100 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCA500 Heures de VolSeuil de 500 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCA1000 Heures de VolSeuil de 1000 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCAPilote de la 8e Escadre de Chasse VirtuelleA publié suffisament de messages sur le forum pour accéder au contenu réservé aux membres de l'école et de la 8e EscadreQualification N1 - A-10C IIQualification N1 obtenue dans le cursus A-10C II de l'ESCA300 SujetsMembre ayant publié un message dans plus de 300 sujets différents2500 Heures de VolSeuil de 2500 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCAVoltigeur aérienMembre ayant fait partie de l'une des patrouilles acrobatiques de l'ESCA



Localisation : Argenteuil/Castelginest
Messages : 678
Date d'inscription : 11/09/2020
 Re: Symbologie IHADSS
Re: Symbologie IHADSS
Mar 14 Nov 2023 - 9:16
J'essayerais de rajouter les images manquante dans les descriptions. Ainsi que de traduire en Français le contenu.
_________________
Killight et Matoche aiment ce message
 RybackQualification N0Qualification N0 obtenue dans le cursus tronc commun (T-45C) de l'ESCAQualification N1 - UH-1HQualification N1 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N2 - UH-1HQualification N2 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N3 - UH-1HQualification N3 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCA100 Heures de VolSeuil de 100 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCA500 Heures de VolSeuil de 500 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCA1000 Heures de VolSeuil de 1000 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCAPilote de la 8e Escadre de Chasse VirtuelleA publié suffisament de messages sur le forum pour accéder au contenu réservé aux membres de l'école et de la 8e EscadreQualification N1 - A-10C IIQualification N1 obtenue dans le cursus A-10C II de l'ESCA300 SujetsMembre ayant publié un message dans plus de 300 sujets différents2500 Heures de VolSeuil de 2500 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCAVoltigeur aérienMembre ayant fait partie de l'une des patrouilles acrobatiques de l'ESCA
RybackQualification N0Qualification N0 obtenue dans le cursus tronc commun (T-45C) de l'ESCAQualification N1 - UH-1HQualification N1 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N2 - UH-1HQualification N2 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N3 - UH-1HQualification N3 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCA100 Heures de VolSeuil de 100 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCA500 Heures de VolSeuil de 500 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCA1000 Heures de VolSeuil de 1000 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCAPilote de la 8e Escadre de Chasse VirtuelleA publié suffisament de messages sur le forum pour accéder au contenu réservé aux membres de l'école et de la 8e EscadreQualification N1 - A-10C IIQualification N1 obtenue dans le cursus A-10C II de l'ESCA300 SujetsMembre ayant publié un message dans plus de 300 sujets différents2500 Heures de VolSeuil de 2500 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCAVoltigeur aérienMembre ayant fait partie de l'une des patrouilles acrobatiques de l'ESCA



Localisation : Argenteuil/Castelginest
Messages : 678
Date d'inscription : 11/09/2020
 Re: Symbologie IHADSS
Re: Symbologie IHADSS
Mar 14 Nov 2023 - 9:37
Bon, traduction libre et approximative
1. Ruban de Cap. Affiche un hémisphère de 180° des caps magnétiques. Les grandes marques sont affichées par incréments de 30° et marquées par une direction cardinale ou un cap dans la valeur des dizaines. Les petites marques sont affichées par incréments de 10°.
2. Cap de l'Aéronef. Affiche une lecture numérique du cap magnétique actuel de l'aéronef par incréments de 1°, superposée sur le Ruban de Cap.
3. Ligne de Mire. La Ligne de Mire est alignée sur l'axe central de l'aéronef et sert de référence à la fois pour le cap de l'aéronef et pour l'indicateur d'inclinaison en mode de symbologie de croisière.
4. Couple du Moteur. Affiche la valeur de couple la plus élevée des deux moteurs, par incréments de 1%. Un cadre sera affiché autour du couple à 98% ou plus. Si la différence entre les valeurs de couple des moteurs dépasse 12%, la lecture numérique du couple clignotera.
5. Ligne d'Horizon. Indique la position et l'orientation de l'horizon par rapport au nez de l'aéronef, référencé au Réticule de Ligne de Visée (LOS). En mode de symbologie de croisière, la Ligne d'Horizon est déplacée en tangage selon un ratio de mouvement de 2:1.
6. Suivi de la Tête. Représente la ligne de données de l'armement (ADL, ou ligne centrale) de l'aéronef ; 0° en azimut et -4.9° en élévation. Le Suivi de la Tête aide les membres d'équipage à maintenir leur position relative à la proue de l'aéronef, surtout dans des conditions de faible luminosité tout en utilisant les capteurs PNVS ou TADS pour le vol et la navigation.
7. Vitesse Indicative. Indique la vitesse air réelle (TAS) de l'aéronef par incréments de 1 nœud, de 0 à 210 nœuds. L'indication de vitesse est encadrée si la vitesse air dépasse la VNE.
8. Échelle de Tangage. Indique l'attitude de tangage de l'aéronef en mode de symbologie de croisière. Les incréments de l'échelle de tangage sont affichés à ±10°, ±20°, ±30°, ±45° et ±60° de tangage.
9. Statut du Point de Cheminement. Affiche le point sélectionné pour la navigation, sa distance en kilomètres ou en milles nautiques et le temps estimé de trajet (ETE).
10. Vitesse Sol. Indique la vitesse sur la surface par incréments de 1 nœud, uniquement en modes de symbologie de croisière et de transition, et uniquement lorsque l'INU principal est aligné.
11. Indicateur d'Inclinaison Latérale. Indique l'inclinaison latérale par rapport à l'horizon en mode de symbologie de croisière.
12. Altitude Barométrique. Indique l'altitude barométrique en mode de symbologie de croisière.
13. Vecteur de Trajectoire de Vol. Le Vecteur de Trajectoire de Vol (FPV) représente le point vers lequel l'hélicoptère vole. C'est une représentation tridimensionnelle du vecteur de vitesse de l'aéronef. Le FPV n'est pas affiché en modes de symbologie de stationnaire ou de montée rapide, si la vitesse tridimensionnelle est <5 nœuds, ou si l'aéronef est posé au sol.
14. Indicateur de Vitesse Verticale (VSI). L'indicateur de vitesse verticale se déplace le long de l'échelle de taux de montée pour indiquer la vitesse verticale.
15. Échelle de Taux de Montée. Les grandes marques sont placées à 0, ±500 et ±1,000 pieds par minute (fpm). Les petites marques sont placées par incréments de 100 fpm entre 0 et ±500 fpm. Lorsque le taux de montée/descente dépasse ±1,000 fpm, une lecture numérique de la valeur la plus proche de 100 fpm est affichée à côté des grandes marques de 1,000 fpm.
16. Altitude Radar. Indique l'altitude détectée par radar au-dessus du niveau du sol de 0 à 1,428 pieds.
17. Indicateur de Glissade. Indique si l'aéronef est en vol coordonné. Si la bille est centrée entre les marques, l'aéronef est en vol coordonné, minimisant la traînée.
18. Cap de Commande. Indique le cap magnétique vers la Navigation Fly-To Cue en modes de symbologie de croisière, de transition ou de stationnaire.
19. Température Turbine du Moteur (TGT). Affiche la température la plus élevée des indications de température de la turbine des deux moteurs.
20. Réticule de Ligne de Visée (LOS). Indique la ligne de visée du casque du membre d'équipage.
21. Navigation Fly-To Cue. Indique l'emplacement du point actuellement sélectionné pour la navigation.
22. Statut G. Affiche la force G mesurée par l'accéléromètre sur l'aéronef.
23. Boîte de Champ de Vue (FOV). La boîte FOV indique la position relative de la ligne de visée du casque du membre d'équipage dans la boîte de champ de regard plus large.
24. Boîte de Champ de Regard (FOR). La boîte FOR indique les limites d'azimut pour la tourelle du capteur de vision nocturne du membre d'équipage.
25. Capteur Alternatif. Indique le cap magnétique de la vue sélectionnée du membre d'équipage opposé.
26. Réticule de Ligne de Visée Ciblée. Indique l'emplacement virtuel de la source d'acquisition sélectionnée du membre d'équipage.
27. Points de Ciblage. Indiquent la direction du quadrant de la source d'acquisition sélectionnée pour "cibler" la position du casque du membre d'équipage par rapport au Réticule de Ligne de Visée Ciblée.
28. Point de Ciblage. Indique l'emplacement relatif de la source d'acquisition sélectionnée dans la boîte de champ de regard.
29. Cueillette de l'Accélération. Indique la magnitude et la direction de l'accélération de l'aéronef.
30. Vecteur de Vitesse. Indique la direction et la magnitude bidimensionnelles de la vitesse de l'aéronef sur la surface.
31. Ruban Altimètre Radar. Affiche l'altitude au-dessus du niveau du sol dans un format "analogique".
32. Boîte de Montée Rapide. La Boîte de Montée Rapide représente une boîte octogonale de 12 pieds de large ancrée à une position sur la surface sous l'hélicoptère.
33. Affichage Haute Action. L'affichage Haute Action est affiché à la fois en symbologie de vol et d'armement, fournissant des messages de priorité sur l'état du viseur et de l'arme à l'équipage pour le ciblage et l'emploi des armes.
1. Ruban de Cap. Affiche un hémisphère de 180° des caps magnétiques. Les grandes marques sont affichées par incréments de 30° et marquées par une direction cardinale ou un cap dans la valeur des dizaines. Les petites marques sont affichées par incréments de 10°.
2. Cap de l'Aéronef. Affiche une lecture numérique du cap magnétique actuel de l'aéronef par incréments de 1°, superposée sur le Ruban de Cap.
3. Ligne de Mire. La Ligne de Mire est alignée sur l'axe central de l'aéronef et sert de référence à la fois pour le cap de l'aéronef et pour l'indicateur d'inclinaison en mode de symbologie de croisière.
4. Couple du Moteur. Affiche la valeur de couple la plus élevée des deux moteurs, par incréments de 1%. Un cadre sera affiché autour du couple à 98% ou plus. Si la différence entre les valeurs de couple des moteurs dépasse 12%, la lecture numérique du couple clignotera.
5. Ligne d'Horizon. Indique la position et l'orientation de l'horizon par rapport au nez de l'aéronef, référencé au Réticule de Ligne de Visée (LOS). En mode de symbologie de croisière, la Ligne d'Horizon est déplacée en tangage selon un ratio de mouvement de 2:1.
6. Suivi de la Tête. Représente la ligne de données de l'armement (ADL, ou ligne centrale) de l'aéronef ; 0° en azimut et -4.9° en élévation. Le Suivi de la Tête aide les membres d'équipage à maintenir leur position relative à la proue de l'aéronef, surtout dans des conditions de faible luminosité tout en utilisant les capteurs PNVS ou TADS pour le vol et la navigation.
7. Vitesse Indicative. Indique la vitesse air réelle (TAS) de l'aéronef par incréments de 1 nœud, de 0 à 210 nœuds. L'indication de vitesse est encadrée si la vitesse air dépasse la VNE.
8. Échelle de Tangage. Indique l'attitude de tangage de l'aéronef en mode de symbologie de croisière. Les incréments de l'échelle de tangage sont affichés à ±10°, ±20°, ±30°, ±45° et ±60° de tangage.
9. Statut du Point de Cheminement. Affiche le point sélectionné pour la navigation, sa distance en kilomètres ou en milles nautiques et le temps estimé de trajet (ETE).
10. Vitesse Sol. Indique la vitesse sur la surface par incréments de 1 nœud, uniquement en modes de symbologie de croisière et de transition, et uniquement lorsque l'INU principal est aligné.
11. Indicateur d'Inclinaison Latérale. Indique l'inclinaison latérale par rapport à l'horizon en mode de symbologie de croisière.
12. Altitude Barométrique. Indique l'altitude barométrique en mode de symbologie de croisière.
13. Vecteur de Trajectoire de Vol. Le Vecteur de Trajectoire de Vol (FPV) représente le point vers lequel l'hélicoptère vole. C'est une représentation tridimensionnelle du vecteur de vitesse de l'aéronef. Le FPV n'est pas affiché en modes de symbologie de stationnaire ou de montée rapide, si la vitesse tridimensionnelle est <5 nœuds, ou si l'aéronef est posé au sol.
14. Indicateur de Vitesse Verticale (VSI). L'indicateur de vitesse verticale se déplace le long de l'échelle de taux de montée pour indiquer la vitesse verticale.
15. Échelle de Taux de Montée. Les grandes marques sont placées à 0, ±500 et ±1,000 pieds par minute (fpm). Les petites marques sont placées par incréments de 100 fpm entre 0 et ±500 fpm. Lorsque le taux de montée/descente dépasse ±1,000 fpm, une lecture numérique de la valeur la plus proche de 100 fpm est affichée à côté des grandes marques de 1,000 fpm.
16. Altitude Radar. Indique l'altitude détectée par radar au-dessus du niveau du sol de 0 à 1,428 pieds.
17. Indicateur de Glissade. Indique si l'aéronef est en vol coordonné. Si la bille est centrée entre les marques, l'aéronef est en vol coordonné, minimisant la traînée.
18. Cap de Commande. Indique le cap magnétique vers la Navigation Fly-To Cue en modes de symbologie de croisière, de transition ou de stationnaire.
19. Température Turbine du Moteur (TGT). Affiche la température la plus élevée des indications de température de la turbine des deux moteurs.
20. Réticule de Ligne de Visée (LOS). Indique la ligne de visée du casque du membre d'équipage.
21. Navigation Fly-To Cue. Indique l'emplacement du point actuellement sélectionné pour la navigation.
22. Statut G. Affiche la force G mesurée par l'accéléromètre sur l'aéronef.
23. Boîte de Champ de Vue (FOV). La boîte FOV indique la position relative de la ligne de visée du casque du membre d'équipage dans la boîte de champ de regard plus large.
24. Boîte de Champ de Regard (FOR). La boîte FOR indique les limites d'azimut pour la tourelle du capteur de vision nocturne du membre d'équipage.
25. Capteur Alternatif. Indique le cap magnétique de la vue sélectionnée du membre d'équipage opposé.
26. Réticule de Ligne de Visée Ciblée. Indique l'emplacement virtuel de la source d'acquisition sélectionnée du membre d'équipage.
27. Points de Ciblage. Indiquent la direction du quadrant de la source d'acquisition sélectionnée pour "cibler" la position du casque du membre d'équipage par rapport au Réticule de Ligne de Visée Ciblée.
28. Point de Ciblage. Indique l'emplacement relatif de la source d'acquisition sélectionnée dans la boîte de champ de regard.
29. Cueillette de l'Accélération. Indique la magnitude et la direction de l'accélération de l'aéronef.
30. Vecteur de Vitesse. Indique la direction et la magnitude bidimensionnelles de la vitesse de l'aéronef sur la surface.
31. Ruban Altimètre Radar. Affiche l'altitude au-dessus du niveau du sol dans un format "analogique".
32. Boîte de Montée Rapide. La Boîte de Montée Rapide représente une boîte octogonale de 12 pieds de large ancrée à une position sur la surface sous l'hélicoptère.
33. Affichage Haute Action. L'affichage Haute Action est affiché à la fois en symbologie de vol et d'armement, fournissant des messages de priorité sur l'état du viseur et de l'arme à l'équipage pour le ciblage et l'emploi des armes.
Killight et Matoche aiment ce message
 KillightPrésident
KillightPrésidentAssociation ESCA
 300 SujetsMembre ayant publié un message dans plus de 300 sujets différentsPilote de la 8e Escadre de Chasse VirtuelleA publié suffisament de messages sur le forum pour accéder au contenu réservé aux membres de l'école et de la 8e EscadreQualification N0Qualification N0 obtenue dans le cursus tronc commun (T-45C) de l'ESCAQualification N1 - UH-1HQualification N1 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N2 - UH-1HQualification N2 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N3 - UH-1HQualification N3 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N1 - Mirage 2000CQualification N1 obtenue dans le cursus Mirage 2000C de l'ESCA100 Heures de VolSeuil de 100 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCA500 Heures de VolSeuil de 500 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCA1000 Heures de VolSeuil de 1000 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCA2500 Heures de VolSeuil de 2500 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCAVoltigeur aérienMembre ayant fait partie de l'une des patrouilles acrobatiques de l'ESCA
300 SujetsMembre ayant publié un message dans plus de 300 sujets différentsPilote de la 8e Escadre de Chasse VirtuelleA publié suffisament de messages sur le forum pour accéder au contenu réservé aux membres de l'école et de la 8e EscadreQualification N0Qualification N0 obtenue dans le cursus tronc commun (T-45C) de l'ESCAQualification N1 - UH-1HQualification N1 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N2 - UH-1HQualification N2 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N3 - UH-1HQualification N3 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N1 - Mirage 2000CQualification N1 obtenue dans le cursus Mirage 2000C de l'ESCA100 Heures de VolSeuil de 100 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCA500 Heures de VolSeuil de 500 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCA1000 Heures de VolSeuil de 1000 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCA2500 Heures de VolSeuil de 2500 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCAVoltigeur aérienMembre ayant fait partie de l'une des patrouilles acrobatiques de l'ESCA


Localisation : ELLX
Messages : 3110
Date d'inscription : 10/09/2020
 Re: Symbologie IHADSS
Re: Symbologie IHADSS
Mar 14 Nov 2023 - 10:38
Oh wow merci @Ryback !! 
Matoche aime ce message
 MatocheQualification N1 - UH-1HQualification N1 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N2 - UH-1HQualification N2 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N3 - UH-1HQualification N3 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCA100 Heures de VolSeuil de 100 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCAPilote de la 8e Escadre de Chasse VirtuelleA publié suffisament de messages sur le forum pour accéder au contenu réservé aux membres de l'école et de la 8e Escadre500 Heures de VolSeuil de 500 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCA
MatocheQualification N1 - UH-1HQualification N1 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N2 - UH-1HQualification N2 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCAQualification N3 - UH-1HQualification N3 obtenue dans le cursus UH-1H Huey de l'ESCA100 Heures de VolSeuil de 100 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCAPilote de la 8e Escadre de Chasse VirtuelleA publié suffisament de messages sur le forum pour accéder au contenu réservé aux membres de l'école et de la 8e Escadre500 Heures de VolSeuil de 500 Heures de Vol atteint au sein de l'ESCA

Localisation : Rouen
Messages : 435
Date d'inscription : 10/09/2020
 Re: Symbologie IHADSS
Re: Symbologie IHADSS
Mar 14 Nov 2023 - 18:17
De la lecture en perspective !
Merci.
Biz
Merci.
Biz
Killight aime ce message
Permission de ce forum:
Vous ne pouvez pas répondre aux sujets dans ce forum